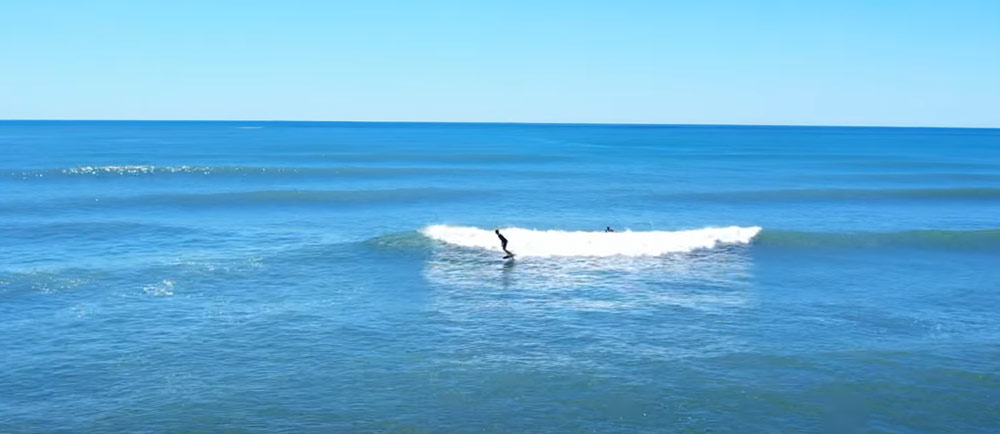
Surfing terms are the basic for surfing sports. Surf sport is a dynamic water sport that requires not only physical fitness but also a mastery of specific techniques and knowledge. In the process of surfing, understanding the specialized terms in surfing is essential for surfers. If you found this article useful, feel free to share it on your social media to help others. Additionally, if you’re interested in customizing your own surf products, please contact our company.

Why Learning Surfing Terms
First, Learning surfing terms greatly enhance learning efficiency. Whether receiving guidance from a coach or self-learning through books and videos, familiarizing yourself with the terminology can help you quickly grasp surfing movements, techniques, and the use of equipment. For example, knowing that “Takeoff” refers to the action of standing up on the surfboard allows you to quickly understand when to start riding the wave.
Secondly, understanding these surfing terms helps improve safety awareness. When surfing, understanding terms like “Tide,” “Ocean current,” and “Wave speed” enables you to assess ocean conditions accurately, avoiding being swept away by currents or encountering waves that are difficult to manage.
Moreover, mastering these surfing terms helps surfers improve their technical skills. Advanced terms like “Backside wave” and “Aerial” refer to higher-level maneuvers, and understanding them allows you to perform better in complex wave conditions.
Finally, surfing is a global sport. Using common terms allows you to communicate better with other surfers in the worldwide surfing community, share experiences, and immerse yourself in the culture of the sport. Overall, understanding these specialized surfing terms is not only the key to improving skills but also the foundation for ensuring surfing safety and enjoyment.
This article will introduce basic surfing equipment, wave-related terms, and various surfing techniques. This knowledge will not only help you understand the surfing environment but also enable you to make the right decisions in different wave conditions.
Surfing Terms Learning

Basic Equipment
- Surfboard: A board used by surfers to ride waves. Ancient surfboards were usually made of foam or wood and came in various shapes and sizes. Modern surfboards are made of polyurethane or polystyrene foam covered with fiberglass cloth, polyester, or epoxy resin.
- Fins: Small fin-like structures attached to the bottom of the surfboard. Fins help surfers control the direction of the surfboard.
- Leash: A cord that connects the surfboard to the surfer’s ankle. The leash prevents the surfboard from drifting away when the surfer falls into the water.
- Wax: A substance applied to the surfboard to increase friction, helping the surfer maintain stability on the board.
Waves
- Wave: The movement of water generated by wind or other natural forces. Surfers use waves to glide on the surface of the sea.
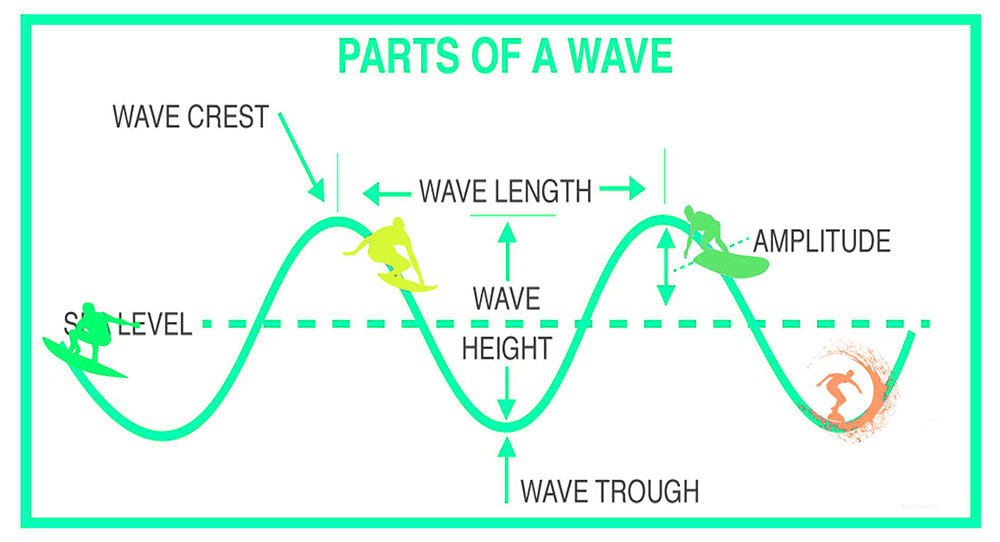
- Wave crest: It is a surfing term that describes the highest point of a wave.
- Wave trough: The lowest point of a wave.
- Wave break: The white foam formed when waves hit the shore.
- Takeoff: The action of a surfer standing up on the surfboard and beginning to ride the wave.
- Surfing: The sport of riding waves on the sea.
- Surfer: A person who participates in surfing.
More Advanced Surfing Terms
- Tube: The hollow part of a wave when it forms a cylindrical shape. Surfers can ride inside the tube.
- Backside wave: It is a surfing term that describes a wave where the surfer rides with their back facing the wave.
- Aerial: It is a surfing term that describes a surfing maneuver where the surfer jumps into the air.
- Wipeout: The action of a surfer falling off the surfboard.
Essential Ocean Information for Surfers
- Tide: The periodic rise and fall of sea levels caused by the gravitational pull of the sun and moon. Tides affect the size and shape of waves.
- Ocean current: The movement of seawater on a large scale. Currents can affect the direction and speed of waves and may carry you away.
- Wind: The force generated by the movement of air. Wind affects the size and shape of waves.
- Wave size: The height of a wave. Wave size affects the difficulty of surfing.
- Wave shape: The shape of a wave. The shape of a wave affects the fun of surfing.
- Seabed: The terrain at the bottom of the ocean. The seabed affects the shape and size of waves.
- Coral reef: A seabed structure formed by coral. Coral reefs affect the shape and size of waves.
- Rock: Solid material on the seabed. Rocks affect the shape and size of waves.
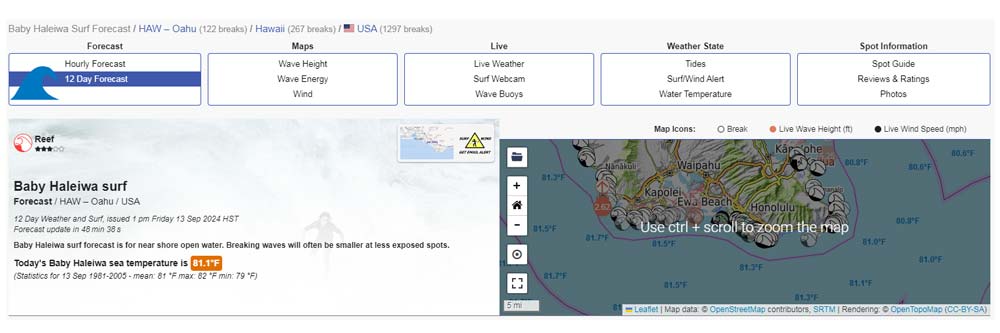
A Surfing Tool Recommended
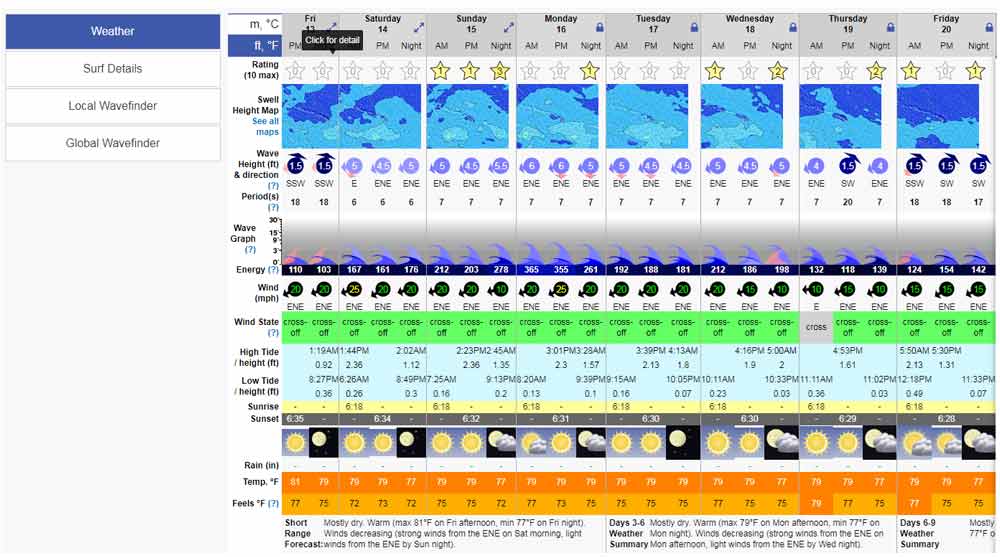
Surf forecast refers to the prediction of ocean conditions that impact surfing, such as wave height, wave period, wind speed, wind direction, tide levels, and weather patterns. Surf forecasting helps surfers determine the best times and locations to surf by providing real-time data and predictions on how waves will behave over the coming hours or days.
Several websites and apps like Surfline, Magicseaweed, and Surf-forecast.com offer detailed surf forecasts. They use a combination of meteorological data, oceanographic modeling, and live webcams to predict wave conditions, tides, and weather, enabling surfers to plan their sessions for optimal conditions.
Techniques Surfing Terms
- Turn: The action of a surfer changing direction on the surfboard.
- Cutback: The action of a surfer turning back toward the wave.
- Re-entry: The action of a surfer accelerating again after completing a turn.
- Flow: The smooth state of a surfer riding on a wave.
Surfing Terms Describing Wave Intensity
- Wave height: The height of a wave. This is the most straightforward term to describe wave intensity.
- Wave shape: The shape of a wave. The shape affects the strength and difficulty of the wave.
- Wave speed: The speed of a wave. The faster the wave, the greater its strength.
- Wave power: The force of a wave. Wave power is the most important factor in determining wave intensity.
Wave Sizes
- Small waves: Waves less than 1 meter high. Suitable for beginners to practice surfing.
- Medium waves: Waves between 1 and 2 meters high. Suitable for surfers with some experience.
- Large waves: Waves between 2 and 3 meters high. Suitable for experienced surfers.
- Giant waves: Waves over 3 meters high. Suitable for professional surfers.
Wave Class in Competitions
- Class 1 wave: Waves less than 1 meter high, with regular shapes, slow speed, and weak force.
- Class 2 wave: Waves between 1 and 2 meters high, with regular shapes, medium speed, and moderate force.
- Class 3 wave: Waves between 2 and 3 meters high, with regular shapes, fast speed, and strong force.
- Class 4 wave: Waves over 3 meters high, with irregular shapes, fast speed, and strong force.
Safety
Surfing requires caution, and you should choose waves that match your ability. Beginners are not suited for reef breaks; it’s better to choose smooth, gentle sandy beaches. Having the right equipment is crucial, so make sure to choose a well-established, reputable surf school with good financial standing. Many smaller or private schools often use old, worn-out equipment to save money, which can significantly affect your surfing experience.
For beginners, it’s essential to learn how to read and recognize waves, surfing term knowledge and avoid riptides. Don’t fight against powerful waves and undercurrents when they keep coming in. You must follow your coach closely, listen to instructions, and choose the best timing and path to enter the wave zone. While surfing, always remember to adjust your breathing. Sometimes the waves are fast, and you’re pressed for time, making it easy to forget to control your breathing.
If you’re frantically paddling, out of breath, and still trying to catch a wave, both your cardiovascular system and muscles won’t be able to keep up. If a big wave slams you down to the bottom, leaving you struggling to resurface, the feeling of suffocation is quite intense.
Conclusion
Mastering the specialized surfing terms in surfing is an important step to becoming an excellent surfer. By understanding basic knowledge like surfboards, fins, tides, and ocean currents, surfers can better interact with their equipment, read the waves, and improve their riding techniques. Moreover, mastering advanced terms like “tube” and “aerial” can help surfers push themselves to new challenges and higher difficulty levels. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced surfer, understanding these surfing terms will help you further improve your surfing skills and enjoy the limitless fun of surfing.